

Wouter Saelens
Assistant Professor, Ghent University
Expert Scientist, Center for Inflammation Research, VIB
The lab uses advanced probabilistic AI models to solve complex immunological puzzles.
We focus on establishing causal links between genes and cell states. We apply key concepts from causal learning to go beyond correlations, and use large-scale perturbational data where possible.
For this we use a systems perspective. Modern perturbational datasets give unique problems for inference and statistics, meaning we push the frontier of deep probabilistic models and amortization. Models are always validated in the lab; a true dream for any aspiring machine learner.
We apply this on urgent problems in immunology, such as immune cell homeostasis, inflammation and oncology.
Latest news
| Jan 01, 2026 | We will soon join VIB.AI as a core member. |
|---|---|
| Jan 01, 2026 | We started our lab! |
Team








Selected publications
-
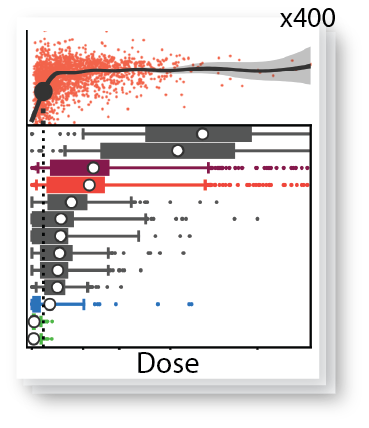 Nature Genetics, Oct 2025
Nature Genetics, Oct 2025A high-throughput technology to study the effect of transcription factor dose. Applied to reprogramming, it reveals how TF dose affects cell fate heterogeneity.
-
 Journal of Open Source Software, Apr 2025
Journal of Open Source Software, Apr 2025A clean and easy way to make complex heatmaps in Python, R and Javascript.
-
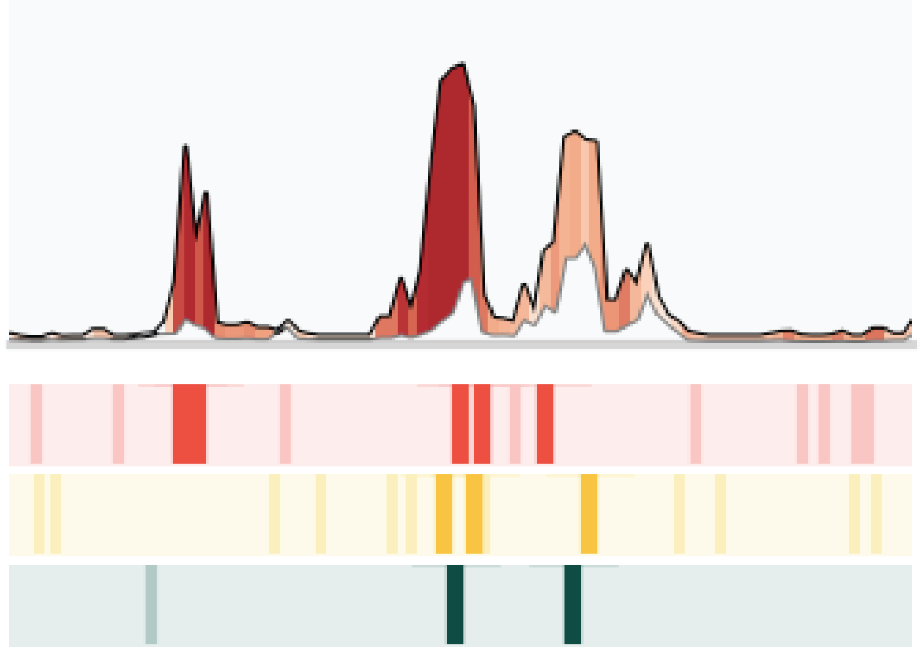 Nature Communications, Jan 2025
Nature Communications, Jan 2025A scale-adaptive machine learning method to link single-cell chromatin accessibility to gene expression. Outperforms peak- and window-based methods by a large margin.
-
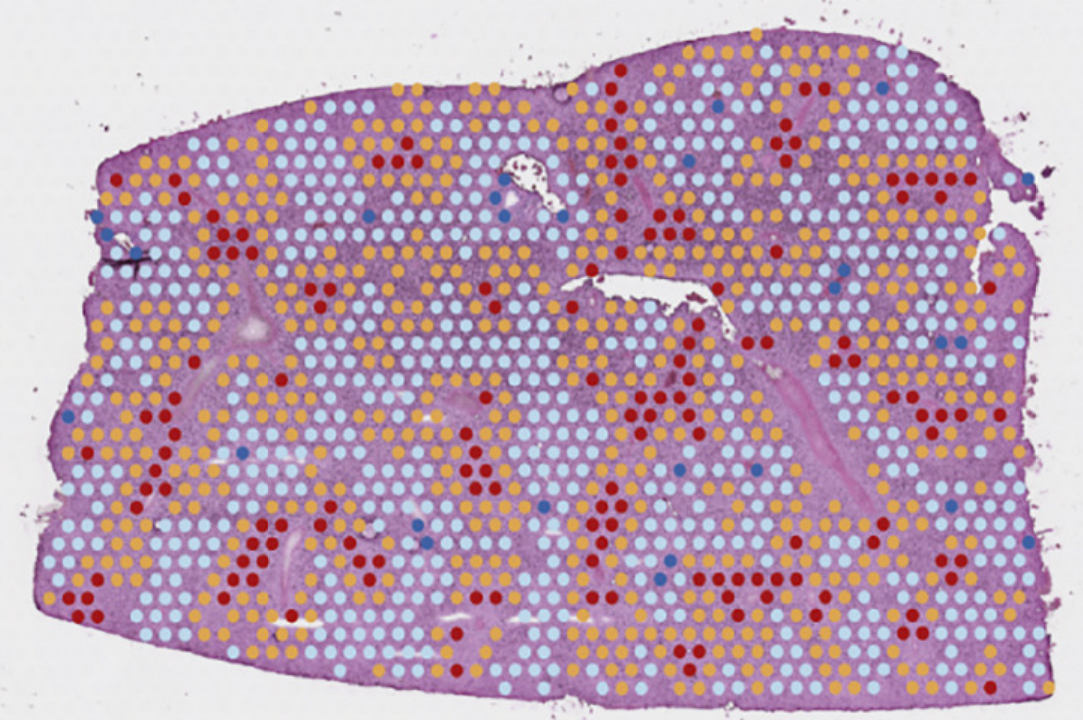 Cell, Jan 2022
Cell, Jan 2022One of the first comprehensive liver cell atlases combining single-cell and spatial transcriptomics with proteomics. Beside being a key resource, it reveals distinct macrophage niches conserved across species.
-
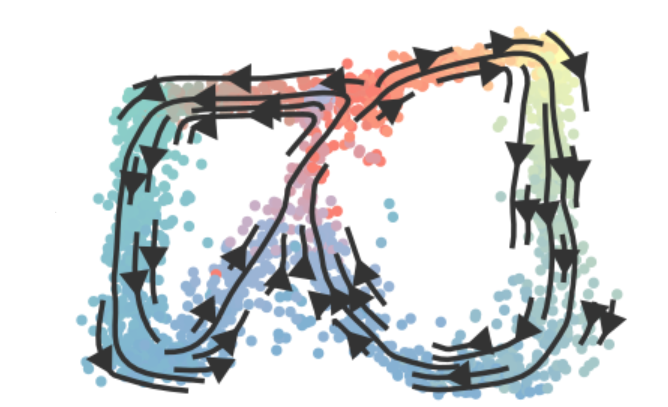 Nature Communications, Jun 2021
Nature Communications, Jun 2021A flexible simulator for single-cell multi-omics data, useful for benchmarking computational methods. Builds on a detailed model of gene regulation, splicing, and translation.
-
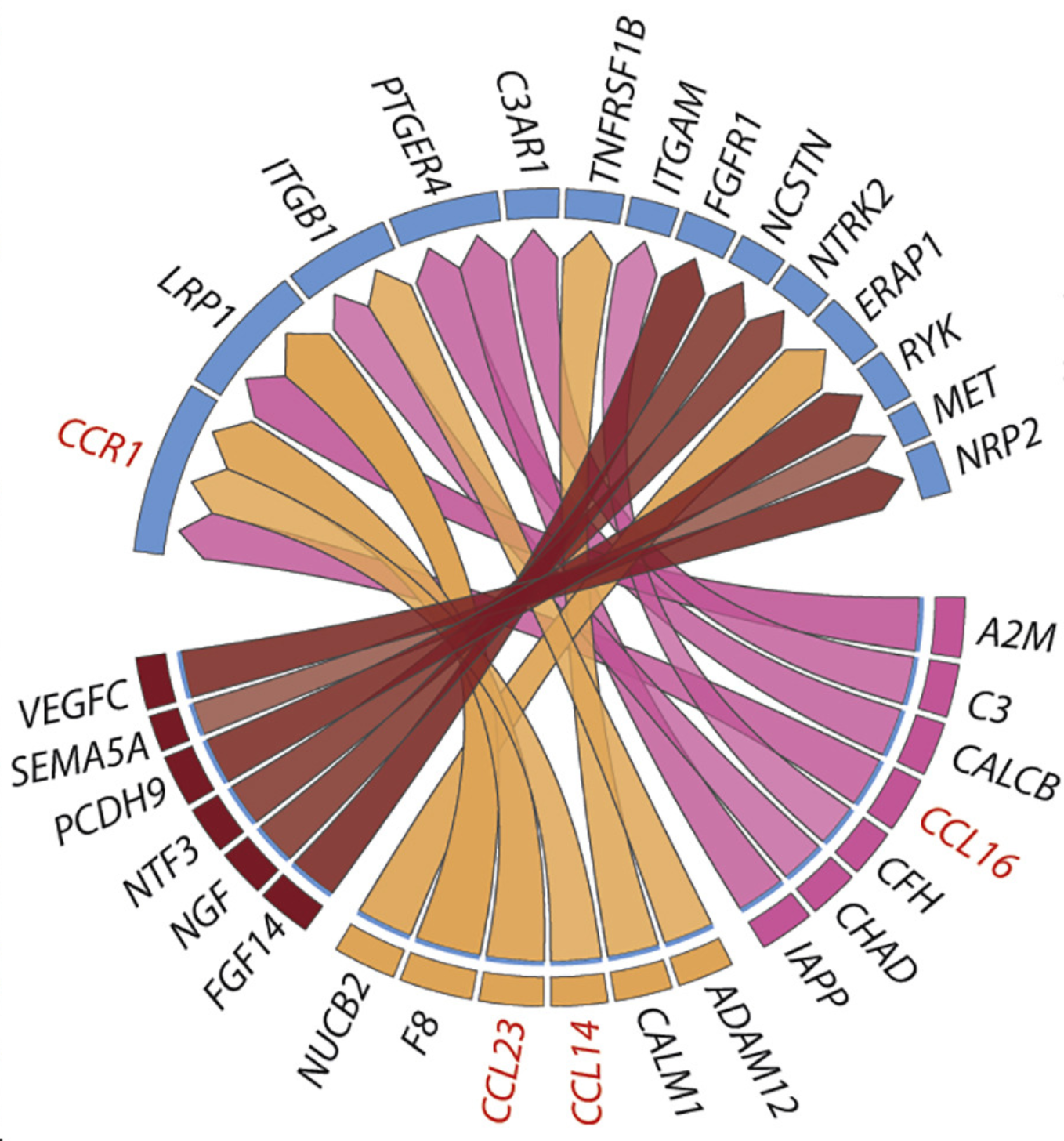 Nature Methods, Feb 2020
Nature Methods, Feb 2020A widely used method to predict cell-cell communication from single-cell data. It uniquely not only looks at ligand-receptor pairs, which is bound to contain false-positives, but also models downstream target gene regulation to ensure the signaling is actively sensed by the cell.
-
 Nature Biotechnology, May 2019
Nature Biotechnology, May 2019The reference benchmark paper for single-cell trajectory inference methods. People love them or hate them, but everyone uses them.
-
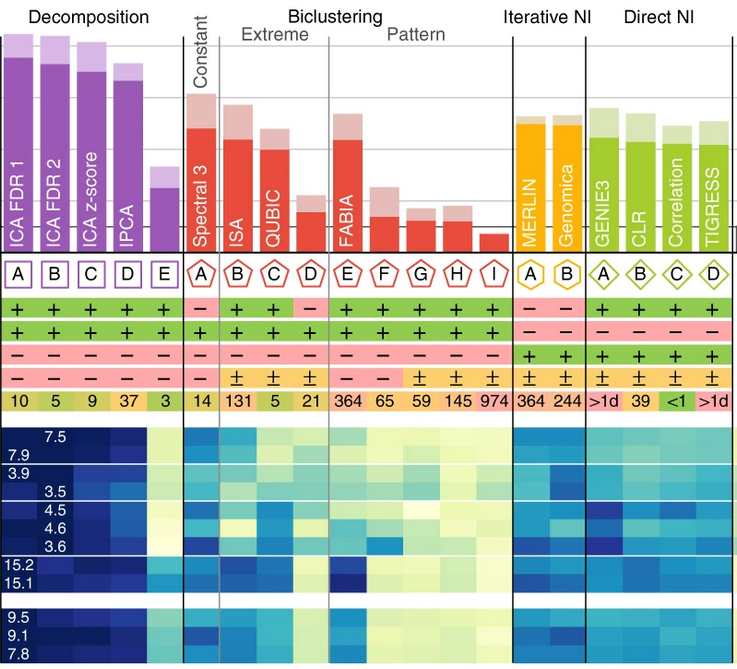 Nature Communications, Mar 2018
Nature Communications, Mar 2018Not all module detection methods are created equal: decomposition methods work best - if you can handle the more complex interpretation.